@AICCRA
On March 8th, the World Bank announced a $40 million funding for the Accelerating the Impact of Climate Research in Africa (AICCRA) project, an initiative designed to promote climate-smart agricultural technologies and strengthen food security in six African countries: Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Mali, Senegal, and Zambia.
This project, overseen by the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR), a global partnership of international organizations working on food security, aims to support the validation of agricultural innovations through pilot experiments. It will also facilitate the production and sharing of knowledge, as well as the establishment of a regional hub dedicated to fertilizers and soil health in West Africa.
The new funding from the World Bank will also strengthen partnerships for service delivery in beneficiary countries. It will support the creation of a specific regional hub for fertilizers and soil health in West Africa, with the aim of improving agricultural fertility and climate resilience in the region in the long term.
In addition to the financial support from the World Bank, other partners have committed to supporting the AICCRA project. The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation plans to provide parallel funding of $18.8 million, while the Office Cherifien des Phosphates (OCP) will contribute $5 million to support the new hub dedicated to soil fertility.
According to Boutheina Guermazi, Director of Regional Integration for Africa and the Middle East at the World Bank, this collaboration demonstrates a shared commitment to addressing the challenges posed by climate change and soil degradation in Africa. She emphasizes that the impacts of climate change on food security require regional solutions and strong partnerships to achieve sustainable outcomes and reduce poverty in a viable long-term environment.
Innovative climate-smart agricultural solutions
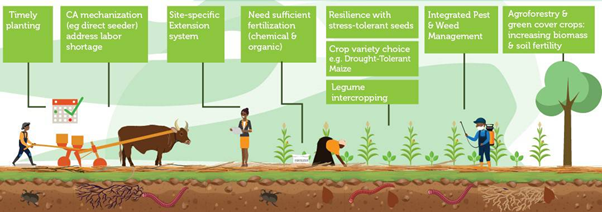
Climate-smart agricultural technologies can play a vital role in promoting food security, especially in regions facing increasing climate challenges. By integrating innovative approaches such as collecting and analyzing meteorological data, efficient use of water resources, and developing crops resistant to extreme climate conditions, these technologies enable farmers to better adapt to environmental changes and maximize yields.
By applying climate-smart agricultural practices, farmers can optimize production while preserving natural resources and reducing their ecological footprint. This not only ensures an adequate availability of food but also strengthens the resilience of food systems to climate shocks and fluctuations in agricultural product prices.
As part of the World Bank-funded AICCRA project, the focus is on deploying such technologies in six African countries, where the effects of climate change are often felt more acutely. By investing in innovative and climate-adapted agricultural solutions, this project aims to ensure sustainable food production and improve food security for local populations.